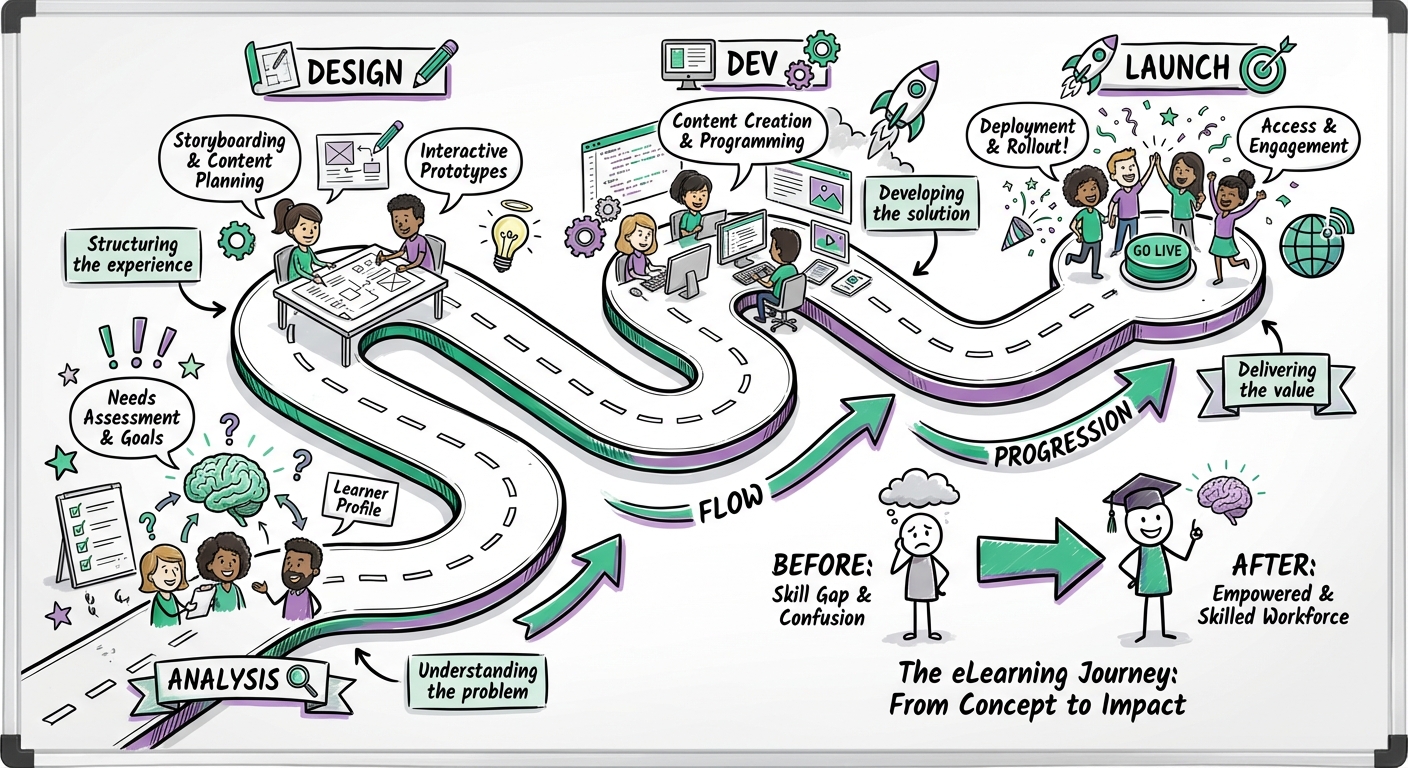
eLearning Development Process Step-by-Step: From Concept to Launch
TL;DR: The eLearning development process transforms training needs into digital learning experiences through 8 key stages: Analysis, Design, Content Development, Technical Development, Implementation, Evaluation, Maintenance, and ongoing Project Management. Success requires a balance of instructional strategy, technical stability, and stakeholder alignment, typically spanning a 3-6 month timeline for custom courses.
Creating effective eLearning isn't just about converting PowerPoint slides into a digital format. It is a systematic engineering process that transforms learning objectives into engaging, measurable educational experiences. Whether you are an L&D professional launching your first course or scaling an enterprise training program, understanding the full lifecycle is crucial for ROI.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the eLearning development process—an expanded view of the traditional ADDIE model—from initial concept to post-launch optimization.
Phase 1: Analysis and Planning
Conducting Needs Assessment
The foundation of any successful eLearning project begins with thorough analysis. This phase determines whether eLearning is the right solution (vs. a job aid or policy change) and establishes the project's scope.
Key Analysis Components:
-
Performance Gap Analysis
- Identify current vs. desired performance levels.
- Determine root causes (is it a skill gap or a motivation gap?).
- Assess whether training is the correct intervention.
-
Learner Analysis
- Demographics: Age, role, location, and language.
- Tech Proficiency: Comfort with digital tools.
- Environment: Bandwidth limitations, firewall restrictions, and device access (mobile vs. desktop).
-
Content Analysis
- Source material availability (SME interviews, existing PDFs).
- Regulatory or compliance requirements.
- Content stability (will this information change in 6 months?).
Setting Clear Objectives
Transform business goals into specific, measurable learning objectives using the SMART framework. This is critical for the eventual evaluation phase.
Example Transformation:
- Vague: "Improve customer service."
- SMART: "By course completion, representatives will demonstrate the ability to resolve 90% of common complaints within 3 minutes using the 'HEARD' protocol, as measured by a branched scenario assessment."
Project Planning and Resource Allocation
Create a detailed project plan (often using a Gantt chart) that includes:
| Planning Element | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Timeline | 3–6 months for custom interactive courses. |
| Budget | Development hours, licensing fees, SME billable time. |
| Team Roles | Project Manager, Instructional Designer (ID), eLearning Developer, QA Tester, SME. |
| Milestones | Design Document sign-off, Alpha/Beta reviews, Gold Master launch. |
Phase 2: Instructional Design
Learning Architecture and Strategy
Instructional design (ID) transforms analysis findings into a blueprint. This phase determines how the content will be taught.
Key Design Decisions:
- Learning Modality: Synchronous (live), asynchronous (self-paced), or blended.
- Content Chunking: Breaking complex topics into microlearning modules (5–15 minutes) to reduce cognitive load.
- Assessment Strategy: Deciding between formative assessments (knowledge checks to reinforce learning) and summative assessments (final graded exams).
Creating the Design Document
The Design Document is your contract with stakeholders. It must contain:
- Learning objectives mapped to business goals.
- Target audience profiles.
- Detailed content outline.
- Visual design style guide (branding, fonts, tone).
- Technical specifications (LMS requirements).
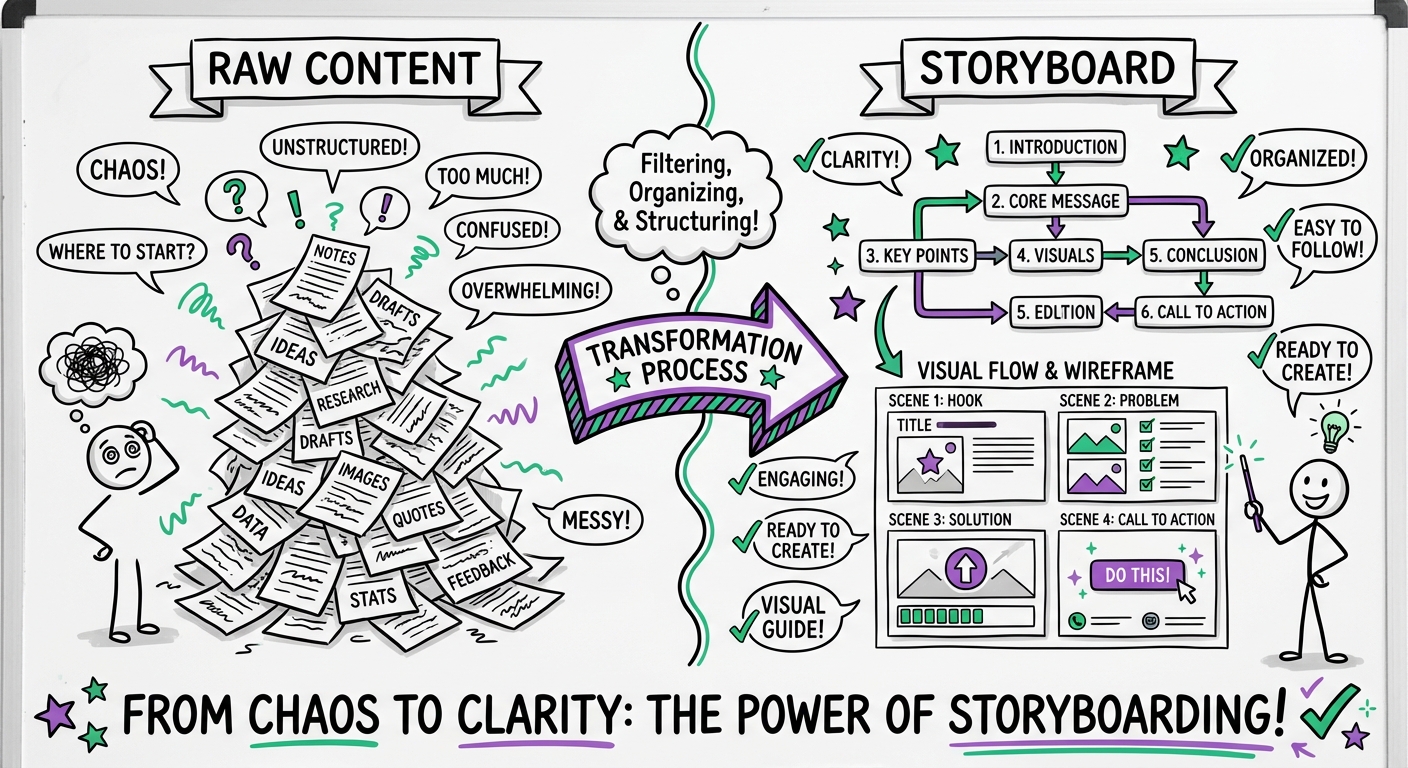
Storyboarding
Storyboards are the "scripts" for your course. They translate the design document into screen-by-screen specifications:
- Text: The exact copy that will appear on screen.
- Audio Script: Narration text for voiceover artists.
- Visual Instructions: Descriptions of images, icons, or animations.
- Programming Notes: Instructions for the developer (e.g., "User must click all 3 tabs to proceed").
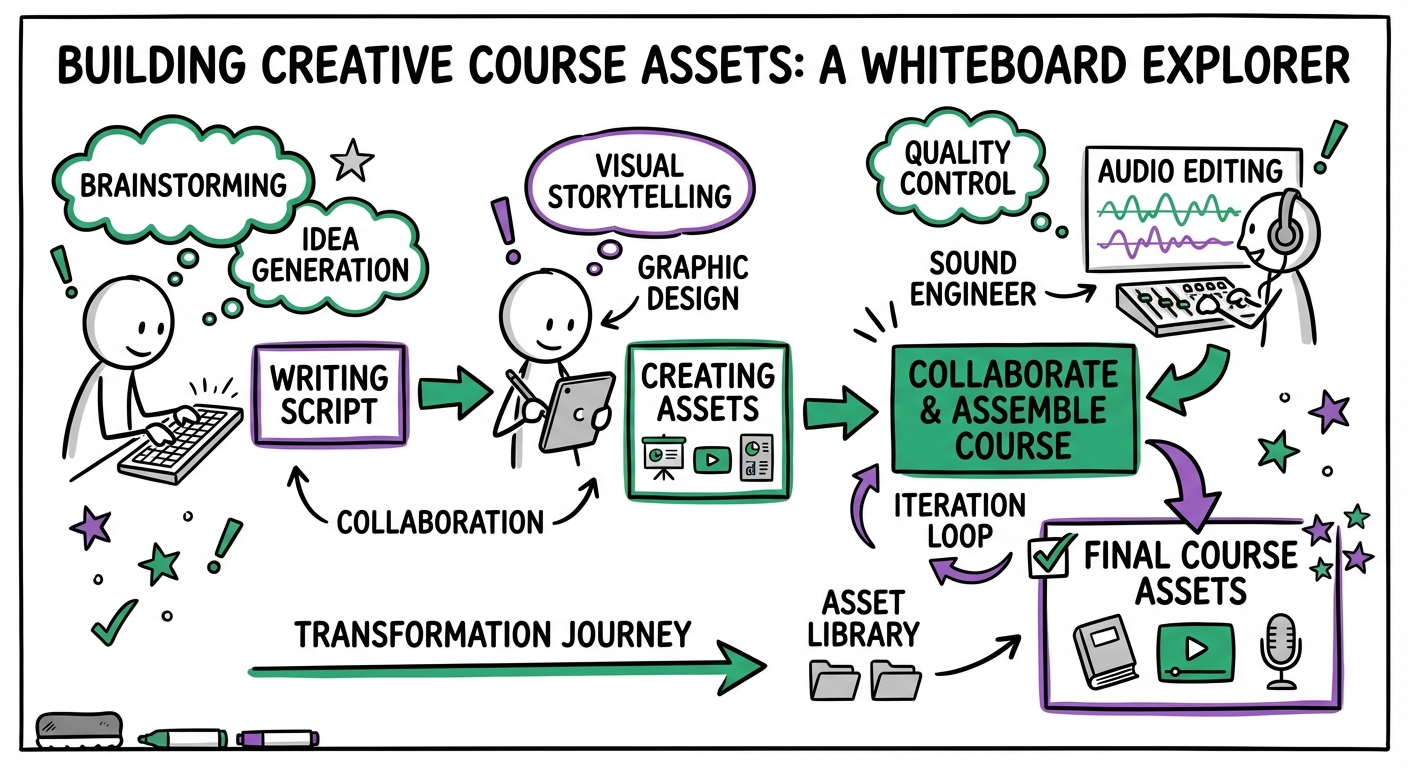
Phase 3: Content Development
Asset Creation
Once the storyboard is approved, the team begins creating the raw assets. This phase often runs parallel to technical development.
- Copywriting: Refining the script for tone and clarity.
- Multimedia Production: Recording voiceovers, filming video, and designing custom graphics/illustrations.
- SME Review: Subject Matter Experts review the raw assets for factual accuracy before they are programmed.
Quality Assurance (Pre-Programming)
Catching errors here is cheaper than catching them later.
- Editorial Review: Grammar, tone, and brand compliance.
- Asset Review: Ensuring images are high-resolution and videos have correct captions.
Phase 4: Technical Development and Authoring
Platform Selection
Choose the authoring tool that fits your design needs:
- Articulate Storyline / Adobe Captivate: Best for complex, custom interactions and software simulations.
- Articulate Rise / Evolve: Best for responsive, mobile-first courses with linear navigation.
- HTML5 Custom: Best for highly unique, gamified experiences requiring bespoke coding.
Programming and Integration
The eLearning Developer assembles the assets into the authoring tool.
- Core Functionality: Building navigation, menus, and player skins.
- Interactivity: Programming triggers, variables, and layers (e.g., drag-and-drop activities, branching scenarios).
- Accessibility: Adding Alt-text, ensuring tab order for keyboard navigation, and verifying color contrast (WCAG 2.1 AA compliance).
Testing and Debugging
- Alpha Review: Internal team checks for functionality (do the buttons work?).
- Beta Review: Stakeholders and a small user group test for usability and content accuracy.
- Gold Master: The final, polished version ready for upload.

Phase 5: Implementation and Deployment
Pre-Launch Preparation
- LMS Configuration: Uploading SCORM/xAPI packages and testing playback in the live environment.
- Support System: Establishing a help desk workflow for learners who have technical issues.
Pilot Testing
Before a full rollout, release the course to a pilot group (10–20 users). Gather data on:
- Technical glitches.
- Confusing questions.
- Time to complete (actual vs. estimated).
Deployment Strategy
- Big Bang: Launch to everyone simultaneously (best for urgent compliance).
- Phased Rollout: Release by department or region (best for large organizations to manage support volume).

Phase 6: Evaluation and Assessment
Measuring Effectiveness
Use the Kirkpatrick Model to evaluate success:
- Level 1 (Reaction): Did learners like it? (Survey data).
- Level 2 (Learning): Did they acquire knowledge? (Assessment scores).
- Level 3 (Behavior): Are they applying it? (Observation/Manager feedback).
- Level 4 (Results): Did it impact the business? (Sales data, reduction in support tickets).
Learning Analytics
Modern LMS and xAPI data can tell you:
- Where learners drop off.
- Which questions are most frequently missed.
- How long learners spend on specific slides.
Phase 7: Maintenance and Updates
Lifecycle Management
eLearning is not "set it and forget it." Content has a shelf life.
- Corrective Maintenance: Fixing bugs reported post-launch.
- Adaptive Maintenance: Updating the course when browsers or the LMS update.
- Content Refresh: Updating facts, policies, or dates (typically annually).
Pro Tip: Build your courses using modular design so you can swap out a single video or slide without rebuilding the entire course.
Overarching Process: Project Management
Agile vs. Waterfall
While ADDIE is often linear (Waterfall), modern eLearning often uses SAM (Successive Approximation Model) or Agile. This involves rapid prototyping and iterative cycles, allowing stakeholders to see and test the course earlier in the process.
Stakeholder Management
- SMEs: Manage their time carefully; they have day jobs.
- Approvers: Define who has final sign-off authority early to avoid "scope creep" (endless changes).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping the Analysis: Building a course when the problem was actually a broken process, not a lack of knowledge.
- "Click Next" Fatigue: Creating a passive page-turner instead of an active learning experience.
- Ignoring Mobile: Failing to test how the course looks on a smartphone.
- Inadequate QA: Launching with broken links or typos, which destroys credibility.
Expert Tips for Success
- Microlearning: Break content into small, digestible chunks.
- Storytelling: Use characters and real-world scenarios rather than abstract theory.
- Accessibility First: Design for accessibility from day one; retrofitting is expensive and difficult.
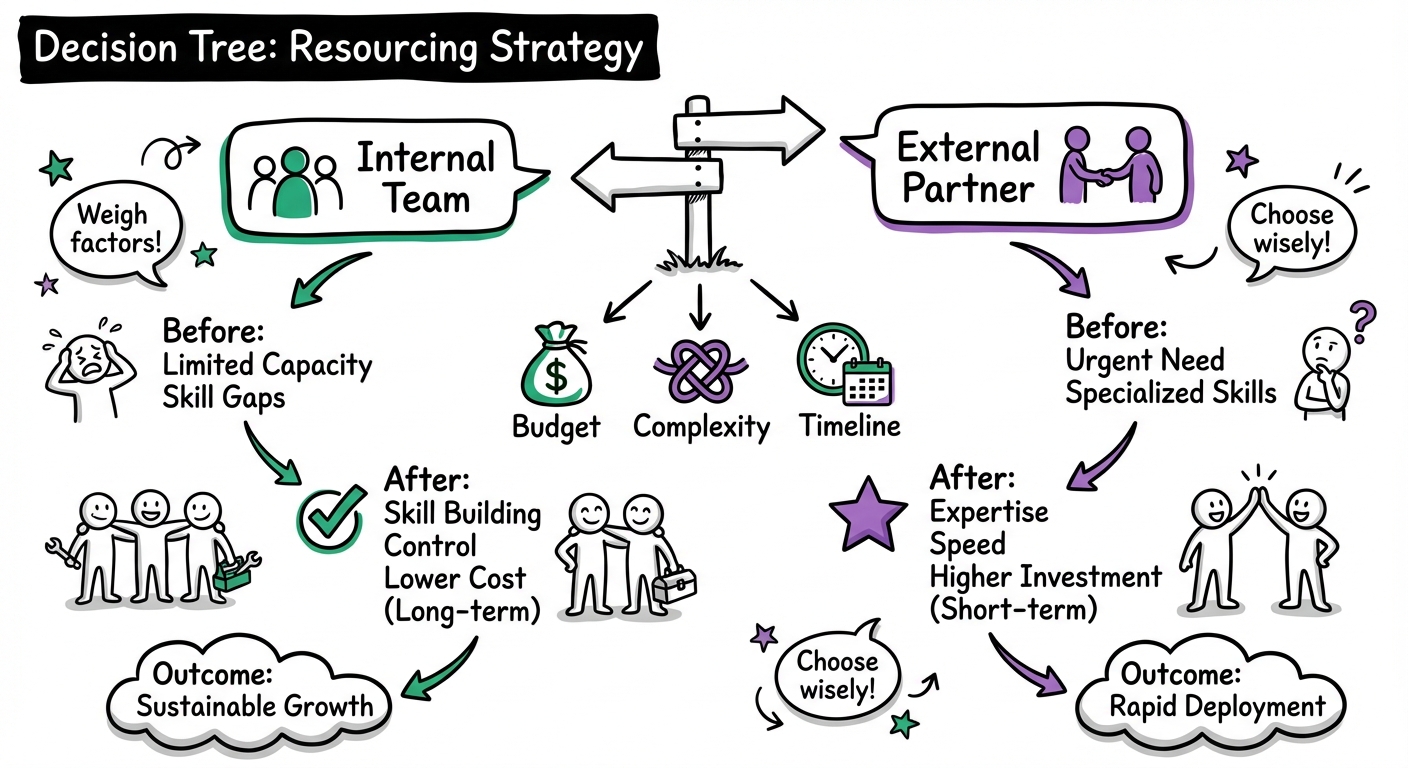
When to Consider Professional Help
Signs You Need an Agency or Freelancer
- High Stakes: The training is for high-value clients or critical compliance.
- Complex Needs: You need advanced gamification, 3D simulations, or VR.
- Capacity: Your internal team is buried, and the deadline is tight.
Finding the Right Partner
Platforms like Learnexus connect you with vetted instructional designers and developers. Look for partners who have a portfolio matching your desired style and experience in your specific industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does the eLearning development process take?
Simple courses: 4–8 weeks. Complex/Custom courses: 3–6 months. Enterprise programs: 6–12 months.
What is the typical budget for eLearning development?
Costs vary by complexity (Level 1: Passive to Level 3: Simulation).
- Internal Development: $5,000–$15,000 per finished hour (calculating salary time).
- External Agency: $10,000–$40,000+ per finished hour of content.
- Freelancers: $3,000–$10,000 per finished hour.
How do I measure ROI?
Formula: (Total Benefits - Total Costs) / Total Costs × 100 = ROI%.
Benefits can include travel savings, reduced instructor time, and productivity gains.
What is the difference between SCORM and xAPI?
- SCORM: The industry standard for tracking completion and score within an LMS. It is reliable but limited.
- xAPI (Tin Can): A newer standard that tracks learning experiences anywhere (mobile, offline, simulations) and provides richer data on learner behavior.
How do I ensure high completion rates?
For mandatory corporate training, completion is usually enforced. For voluntary programs, aim for 60–80% by using:
- Short modules (under 10 mins).
- Manager endorsement.
- Internal marketing campaigns.